Unfortunately, there is no standard for color coding serial lines. You might hope that signal ground is black/brown, though often it is green, or some other random color. TX / RX are often yellow and green, but again you cannot count on this. The only way to know which color is connect to what pin is to test with a multimeter. StarTech.com 2m Black DB9 RS232 Serial Null Modem Cable F/M - DB9 Male to Female - 9 pin Null Modem Cable - 1x DB9 (M), 1x DB9 (F), Black, SCNM9FM2MBK 4.4 out of 5 stars 128 $6.49 $ 6. The pinout of the DB-9 connector can be confusing when cabling an RS232 line. There are a lot of details to consider when arranging the pins between Male and Female connectors on a serial cable or serial.
RS232 DB9 9 Pin Data Serial Cable, Male to Female DB9 Straight Through Extension Cable YOUCHENG for Computers, Printers, Scanners 8.5 Feet 3.8 out of 5 stars 5 $8.99 $ 8. The units have an LED for each signal line in the cable, and the LED lights green or red dependent on the signal state. Our D9 Breakout box is a little more sophisticated - it also allows you to disconnect certain lines in the cable, and to loop signals to their opposite number - good for trying new cable wiring.
Looking for a way to transmit data from one device to another quickly and securely? Thanks to RS232 serial port monitoring hardware, you should have no trouble capturing data and overcoming many of the latency and time-tagging problems commonly associated with traditional dual COM port monitoring solutions.

RS232 serial port monitoring hardware stands out for a number of reasons, including its 9 pin RS232 pinout. This pinout can make a world of difference for successful RS232 serial communications. Thus, it is important to understand how the 9 pin RS232 cable pinout can affect the flow of serial data between devices.
Here's a closer look at how the 9 pin RS232 pinout works and what it means for users who want to transmit data between devices safely and efficiently.
What Is an RS232 9 Pin Pinout?
RS232 monitoring hardware establishes a connection between data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communication equipment (DCE). In order to link these devices, an RS232 D9 pinout is essential, as this pinout will allow you to connect two devices successfully.
9 Pin Serial Connector
An RS232 pinout 9 pin cable features nine pins:
1. Data Carrier Detect – After a data terminal is detected, a signal is sent to the data set that is going to be transmitted to the terminal.
2. Received Data – The data set receives the initial signal via the receive data line (RxD).
3. Transmitted Data – The data terminal gets a signal from the data set, a confirmation that there is a connection between the data terminal and the data set.
4. Data Terminal Ready – A positive voltage is applied to the data terminal ready (DTR) line, a sign that the data terminal is prepared for the transmission of data.
5. Signal Ground – A return for all the signals on a single interface, the signal ground (SG) offers a return path for serial communications. Without SG, serial data cannot be transmitted between devices.
6. Data Set Ready – A positive voltage is applied to the data set ready (DSR) line, which ensures the serial communications between a data terminal and a data set can be completed.

7. Request to Send – A positive voltage indicates the request to send (RTS) can be performed, which means the data set is able to send information to the data terminal without interference.
8. Clear to Send – After a connection has been established between a data terminal and a distant modem, a clear to send (CS) signal ensures the data terminal recognizes that communications can be performed.
9. Ring Indicator – The ring indicator (RI) signal will be activated if a modem that operates as a data set detects low frequency. When this occurs, the data terminal is alerted, but the RI will not stop the flow of serial data between devices.
Understanding the ins and outs of the 9 pin RS232 cable pinout can be challenging for even experienced design services professionals. But with support from a proven engineering team, you can optimize the transmission of data via a RS232 9 pin pinout.
Stratus Engineering supplies a broad array of RS232 hardware monitoring solutions, along with application expertise and extensive hardware and software engineering experience. To learn more how we support electronics and software for embedded systems, please contact us today at 858-663-1841.
RS232 Includes:
RS232 basicsRS232 standardSoftware handshakingSignals & voltage levelsPinouts & connectorsLoopback connectionsRS232 cables
Serial Data standards:Serial data standardsRS422RS449RS48520 mA current loop
Whenever RS232 is used, RS232 cables will be needed to provide the required electrical connection.
These cable can take a variety of forms in terms of the physical methods used for construction as well as the number of connections that are incorporated within the overall RS232 cable.
When constructing a cable, it should be remembered that not all the signals provided within RS232 need to be implemented in a practical RS232 data cable. As a result, designs for a variety of serial data cables may be seen on the Internet and elsewhere.
In addition to this, further confusion is caused by the fact that RS232 was designed to connect modems and terminal devices or teleprinters so that telephone lines could be used to transit data over the telephone system, and serial data cables were required to connect the equipment at the remote end. This intended application for RS232 gives rise to the terminology associated with these serial data connections, i.e. DCE (Data Communications Equipment or Modem) and the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment or teleprinter).
Although many manufacturers agree on the general application of the types of RS232 serial data cables, there is still confusion in many quarters over what may be required. As a result it is always best to be aware of the complications that exist. As a result it may often be necessary to experiment a little.
Serial data cable basics
Pins are assigned within the DTE and DCE such that a '1:1' cable should be used, i.e. on where pin number X at one end is connected to pin number X at the other end and there are no crossovers.
Thus a DTE transmits data on pin 2 and the DCE receivers data on pin 2. Similarly The DTE receives data on pin 3, whereas the DCE transmits on pin 2.
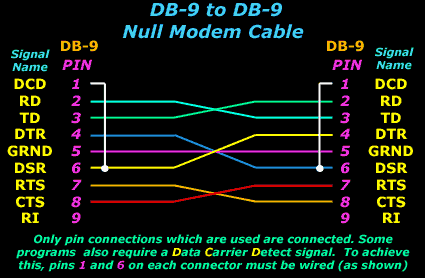
Adopting this approach makes the construction of RS232 serial data cables much easier. It also saves considerable complications by not having to work out which wires to cross over in the serial data cable.
Complications do arise when cables are required to connect two items both configured as the same form of equipment, i.e. both a DTE or both a DCE.
Serial data cable diagrams and pin connections
Different data systems utilise different levels of handshaking when using RS232. Some of the simpler systems just send the data without any hard wired handshaking and as a result the serial data cables required for this are very simple. These systems may utilise the use of software codes such as X-ON / X-OFF, ACK, NAK, etc to provide the handshaking that is required. These systems require serial data cables that incorporate the transmit and receive data lines as well as an earth line. A suitable cable is shown below.
More comprehensive systems may utilise the additional lines provided by RS232. According serial data cables for these systems require the additional lines to be incorporated into the serial data cables for them to operate correctly. A suitable cable is shown below.
The RS232 cable shown above gives the more likely connections seen in an RS232 cable. Some cables could have more connections for additional functionality, but these are rarely used.
RS232 serial port monitoring hardware stands out for a number of reasons, including its 9 pin RS232 pinout. This pinout can make a world of difference for successful RS232 serial communications. Thus, it is important to understand how the 9 pin RS232 cable pinout can affect the flow of serial data between devices.
Here's a closer look at how the 9 pin RS232 pinout works and what it means for users who want to transmit data between devices safely and efficiently.
What Is an RS232 9 Pin Pinout?
RS232 monitoring hardware establishes a connection between data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communication equipment (DCE). In order to link these devices, an RS232 D9 pinout is essential, as this pinout will allow you to connect two devices successfully.
9 Pin Serial Connector
An RS232 pinout 9 pin cable features nine pins:
1. Data Carrier Detect – After a data terminal is detected, a signal is sent to the data set that is going to be transmitted to the terminal.
2. Received Data – The data set receives the initial signal via the receive data line (RxD).
3. Transmitted Data – The data terminal gets a signal from the data set, a confirmation that there is a connection between the data terminal and the data set.
4. Data Terminal Ready – A positive voltage is applied to the data terminal ready (DTR) line, a sign that the data terminal is prepared for the transmission of data.
5. Signal Ground – A return for all the signals on a single interface, the signal ground (SG) offers a return path for serial communications. Without SG, serial data cannot be transmitted between devices.
6. Data Set Ready – A positive voltage is applied to the data set ready (DSR) line, which ensures the serial communications between a data terminal and a data set can be completed.
7. Request to Send – A positive voltage indicates the request to send (RTS) can be performed, which means the data set is able to send information to the data terminal without interference.
8. Clear to Send – After a connection has been established between a data terminal and a distant modem, a clear to send (CS) signal ensures the data terminal recognizes that communications can be performed.
9. Ring Indicator – The ring indicator (RI) signal will be activated if a modem that operates as a data set detects low frequency. When this occurs, the data terminal is alerted, but the RI will not stop the flow of serial data between devices.
Understanding the ins and outs of the 9 pin RS232 cable pinout can be challenging for even experienced design services professionals. But with support from a proven engineering team, you can optimize the transmission of data via a RS232 9 pin pinout.
Stratus Engineering supplies a broad array of RS232 hardware monitoring solutions, along with application expertise and extensive hardware and software engineering experience. To learn more how we support electronics and software for embedded systems, please contact us today at 858-663-1841.
RS232 Includes:
RS232 basicsRS232 standardSoftware handshakingSignals & voltage levelsPinouts & connectorsLoopback connectionsRS232 cables
Serial Data standards:Serial data standardsRS422RS449RS48520 mA current loop
Whenever RS232 is used, RS232 cables will be needed to provide the required electrical connection.
These cable can take a variety of forms in terms of the physical methods used for construction as well as the number of connections that are incorporated within the overall RS232 cable.
When constructing a cable, it should be remembered that not all the signals provided within RS232 need to be implemented in a practical RS232 data cable. As a result, designs for a variety of serial data cables may be seen on the Internet and elsewhere.
In addition to this, further confusion is caused by the fact that RS232 was designed to connect modems and terminal devices or teleprinters so that telephone lines could be used to transit data over the telephone system, and serial data cables were required to connect the equipment at the remote end. This intended application for RS232 gives rise to the terminology associated with these serial data connections, i.e. DCE (Data Communications Equipment or Modem) and the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment or teleprinter).
Although many manufacturers agree on the general application of the types of RS232 serial data cables, there is still confusion in many quarters over what may be required. As a result it is always best to be aware of the complications that exist. As a result it may often be necessary to experiment a little.
Serial data cable basics
Pins are assigned within the DTE and DCE such that a '1:1' cable should be used, i.e. on where pin number X at one end is connected to pin number X at the other end and there are no crossovers.
Thus a DTE transmits data on pin 2 and the DCE receivers data on pin 2. Similarly The DTE receives data on pin 3, whereas the DCE transmits on pin 2.
Adopting this approach makes the construction of RS232 serial data cables much easier. It also saves considerable complications by not having to work out which wires to cross over in the serial data cable.
Complications do arise when cables are required to connect two items both configured as the same form of equipment, i.e. both a DTE or both a DCE.
Serial data cable diagrams and pin connections
Different data systems utilise different levels of handshaking when using RS232. Some of the simpler systems just send the data without any hard wired handshaking and as a result the serial data cables required for this are very simple. These systems may utilise the use of software codes such as X-ON / X-OFF, ACK, NAK, etc to provide the handshaking that is required. These systems require serial data cables that incorporate the transmit and receive data lines as well as an earth line. A suitable cable is shown below.
More comprehensive systems may utilise the additional lines provided by RS232. According serial data cables for these systems require the additional lines to be incorporated into the serial data cables for them to operate correctly. A suitable cable is shown below.
The RS232 cable shown above gives the more likely connections seen in an RS232 cable. Some cables could have more connections for additional functionality, but these are rarely used.
Constructing RS232 cables
There are several methods that can be used to construct RS232 cables and the method chosen should be selected according to the requirements, cost timescales, level of reliability, etc.
The most straightforward is to have two solder type connectors and to wire between them, one to one. This can be time consuming, but often provides a good cable provided a few precautions are adopted.
A second approach is to use an insulation displacement style cable. And connectors. This is exceedingly easy to implement, but may not be as robust or provide the screening needed to protect the integrity of the transmitted data over any distance.
To ensure the cable operates satisfactorily there are a few precautions that can be adopted.
- Use strain relief on connectors: As the RS232 cables could undergo flexing, it is necessary to ensure that good strain relief is provided. Most connectors have options for adding strain relief and this should be adopted.
- Ensure no solder shorts on solder type connectors: When soldering the connectors for the cables it is easy to develop a short as a result of excess solder. Thoroughly inspect and electrically check the cable before use.
- Have a protective sleeve over wiring: With the possibility of many wires being connected, these should be kept under control in a sleeve. There are many types of sleeve that can be sued and these will give protection as well as keeping he wires together.
- Provide screening if cable in high noise environment: Some environments that have high levels of electrical noise may require a screen to be placed over the cable. This can be incorporated as part of the ground system.
While it is possible to buy RS232 serial data cables, it is also easy to manufacture them if the relevant connectors are available. If there are no complications, i.e. they are wires as for a DTE to DCE connection, a serial data cable will simply require one to one connections of the required pins.
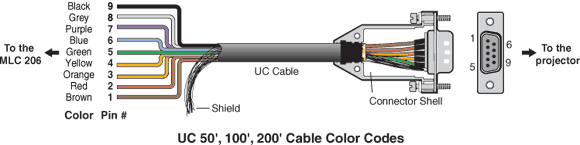
9 Pin Serial Cable Wire Colors List
Wireless & Wired Connectivity Topics:
Mobile Communications basics2G GSM3G UMTS4G LTE5GWiFiIEEE 802.15.4DECT cordless phonesNFC- Near Field CommunicationNetworking fundamentalsWhat is the CloudEthernetSerial dataUSBSigFoxLoRaVoIPSDNNFVSD-WAN
Return to Wireless & Wired Connectivity
